May 24, 2022
Make the most of your drone data with cloud based drone data processing

Drone surveys or "drone as a service" enable enterprises to avail various benefits from drone data. These services essentially help in bridging the gap between worksite managers and surveyors by providing them with the best technology in both hardware and software, along with trained experts in the fields of surveying and photogrammetry.
Drones as a service for any industry have 3 basic components:
- Drone Data Acquisition
- Drone Data Processing
- Analyze and visualise
When we talk about drone data acquisition, there are a few steps as follows:
- Planning Data Acquisition: Before starting a project, a project manager has to plan out the entire survey and plan out the drone missions for proper data collection. A project manager needs to have prerequisite knowledge for mission planning to account for different factors like overlap images, multiple flights, mission/flight management, data management, etc.
- Data Management : A drone will typically capture 500 images in a 1 sq km area. A mining or solar plant worksite is typically much larger, which means proper data management is critical for data quality checks and, later, processing.
- Data Quality Check: Camera calibration, accurate elevation, exposure of the images, overlap etc. are all very important factors for data processing. If these are not checked in the initial stages of processing, the photogrammetric outputs will not be accurate.
- Data transfer: After the initial quality checks are done, the data can be transferred for photogrammetric processing.
Drone survey doesn’t end at Data acquisition. To generate valuable insights from the data and make data driven decisions, the raw images need to be processed and generate Ortho, DSM, DTM and Point Cloud - the basic Photogrammetric outputs.
Here are the steps that a GIS expert needs to take to generate the basic photogrammetric outputs:
- Pre Processing Checks
- Check if the image overlap is proper.
- Check if the AOI is covered with enough tie points for the software to process.
- Check the EXIF files to correct the elevation files.
- Initial Processing
- Align the photos together. As the images are geotagged, they should fall into place corresponding to the coordinates.
- GCP marking
- Whether you are using PPK or RTK drones to capture your data, it is always advised to use GCP as check points to correct the x, y, or z coordinates of the final outputs.
- QC for the final outputs needs to be performed.
- Most photogrammetric software generates reports to show if the outputs are accurate or not. It is still advised to perform some manual checks to check for minute errors as well.
Here are the factors that can cause high error in the Final Photogrammetric Outputs:
Data Acquisition
- Prerequisite Knowledge for Mission Planning
- Pilot skills for dynamic worksite environments.
- Follow the terrain in mission planning.
- Proper GCP placement
- On-Field Data Quality Check
- Weather Conditions for flying a drone
Data Processing
- Exif values for accurate elevation values for each survey
- High error during GCP marking
- Over or underexposed images
- System configuration with high RAM (if we are using a desktop-based processing software)
- Data transfer and data management have to be taken care of while working with surveys for large worksites.
- GIS/Photogrammetric Expertise to handle any errors that might occur.
A typical drone data processing job in AgiSoft Metashape (Photogrammetric processing software) involves these tedious steps:
- Create a new project and upload all your geotagged images.
- Upload Exif files to correct the elevation value.
- Align all the images with respect to their x and y coordinates.
- Check the initial process report: this is a crucial step as a GIS expert can identify the possible errors in the data set.
- Mark GCP This is an optional step depending on the type of drone used. Although a GIS expert always advises including a few GCPs as check points in larger worksites,
- GCP Optimisation to optimise the position of GCPs
- Building a dense point cloud: Point cloud modelling creates a representation of a 3D object with densely placed vertices or points along its surface.
- Building mesh: an optional step which converts the dense point cloud into a 3D mesh with vertices connecting all the points.
- Building DEM to get DSM, which are rasters, Every pixel of these rasters has an elevation value along with x and y coordinates.
- Building Orthomosaic
- GCP error check as the survey needs errors to be as low as possible.
- Classify DEM into above-ground features and ground features to generate DTM.
- Basic photogrammetric outputs are ready.
A typical Drone Data Processing of 1 sqkm, which comprises approximately 500 images in Agisoft Metashape, takes more than 24 hours to get processed.
Although a GIS/Photogrammetry expert can batch process a part of the above mentioned steps, these are the disadvantages of processing your drone data in a desktop-based photogrammetric software:
- High-end system configuration is needed, which can get expensive.
- If GIS/experts are needed, they typically know the know-how of the photogrammetric software and will be able to correct errors in the data.
- Only one dataset can be processed at a time: Photogrammetric software usually uses the entire RAM, which means only one dataset can be processed at a time.
- It takes longer to process the data as the software will use the available RAM only. The processing gets slower.
- Memory space and data management become a problem: Photogrammetric processing files can be as big as 500 GB or more. Multiple projects of this size can cause memory space issues.
- Data can only be accessed by one system or a few systems that are interconnected.
A data set of 5000 images will take about 48 hours to process in AgiSoft, whereas Spectra’s Cloud Based Mapping solution takes 24 hours to deliver the same outputs.
Enter Skylark's cloud platform
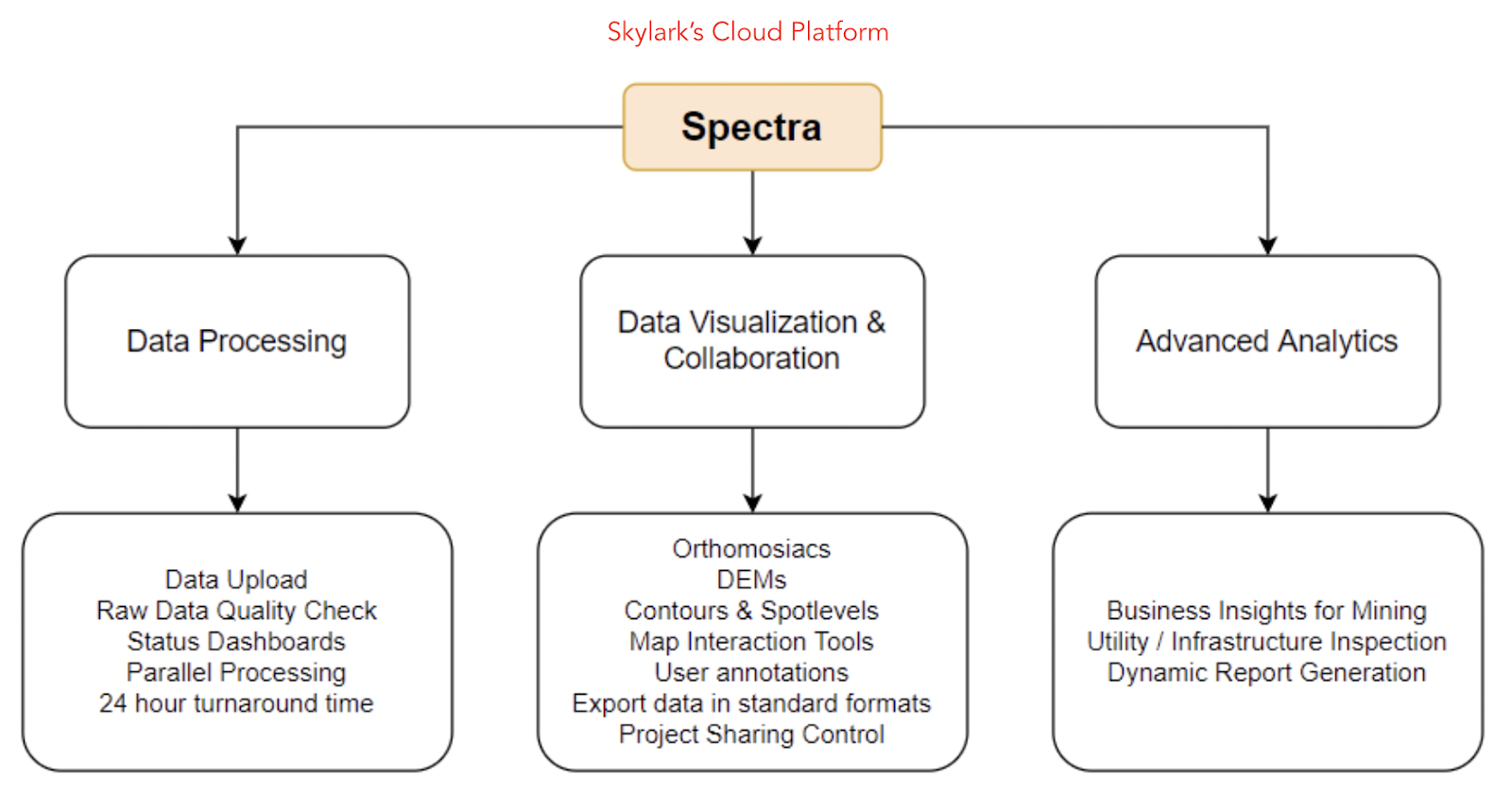
Spectra is an Intelligent Drone Data Management Platform to accelerate asset profitability by helping Enterprises plan better, construct faster and sustain longer.
Mapping Solution:
With Spectra’a Mapping Solution, one can process drone data in a few clicks :
1. Collect Data Yourself
Collect the drone data with any of our recommended drone models at any frequency that suits your mapping needs. We provide 24x7 support and Our drone flight execution and verification software for free.
2. Process Data Automatically
Upload your drone images and GCP data to our platform, we will process and deliver the data to you in 24 hours*
3. Visualise and Analyse Worksite
Our platform enables you to visualize your data, analyse and measure your worksite and download reports, all on your browser
The advantages of a cloud-based solution are:
- Easy data access: As Spectra is a web-based cloud platform, all data is stored in a centralised repository. This data can be easily accessed by any device at any time.
- Processing multiple datasets at once: As this is a cloud platform, it is highly scalable.
- Faster data processing: As cloud platforms have much better performing servers, the data processing is much faster.
- Low upfront cost: high-end computers and GIS/Photogrammetry experts are expensive. A cloud platform like Spectra can reduce the upfront cost drastically.
- GIS/Photogrammetric experts are not required. Spectra is powered by AI technology and can hence help you with processing the data without the absolute need of a GIS or photogrammetry expert.


